
If a < 1, the function stretches with respect to the x-axis.Ĭonsider a parent function y = x 2 +x. If a 1, the function shrinks with respect to the x-axis. If a > 1, the function stretches with respect to the y-axis. The vertical stretch is given by the equation y = a.f(x). The transformation that causes the 2-d shape to stretch or shrink vertically or horizontally by a constant factor is called the dilation.
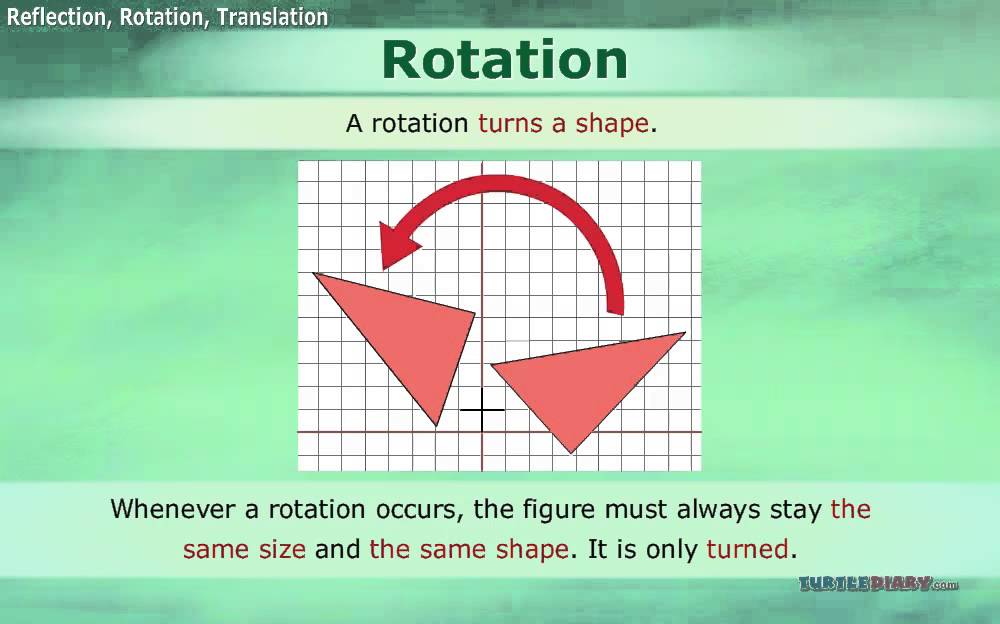
The transformation that is taken place here is from (x,y) → (-x, 2-y) Let us observe the rule of rotation being applied here from (x,y) to each vertex. In the function graph below, we observe the transformation of rotation wherein the pre-image is rotated to 180º at the center of rotation at (0,1). The general rule of transformation of rotation about the origin is as follows. The shape rotates counter-clockwise when the number of degrees is positive and rotates clockwise when the number of degrees is negative. The transformation that rotates each point in the shape at a certain number of degrees around that point is called rotation. The transformation of f(x) is g(x) = - x 3 that is the reflection of the f(x) about the x-axis. Here is the graph of a quadratic function that shows the transformation of reflection. Thus the line of reflection acts as a perpendicular bisector between the corresponding points of the image and the pre-image. If point A is 3 units away from the line of reflection to the right of the line, then point A' will be 3 units away from the line of reflection to the left of the line. Every point (p,q) is reflected onto an image point (q,p). When the points are reflected over a line, the image is at the same distance from the line as the pre-image but on the other side of the line. The type of transformation that occurs when each point in the shape is reflected over a line is called the reflection. The transformation f(x) = (x+2) 2 shifts the parabola 2 steps right. This pre-image in the first function shows the function f(x) = x 2. We can apply the transformation rules to graphs of quadratic functions.
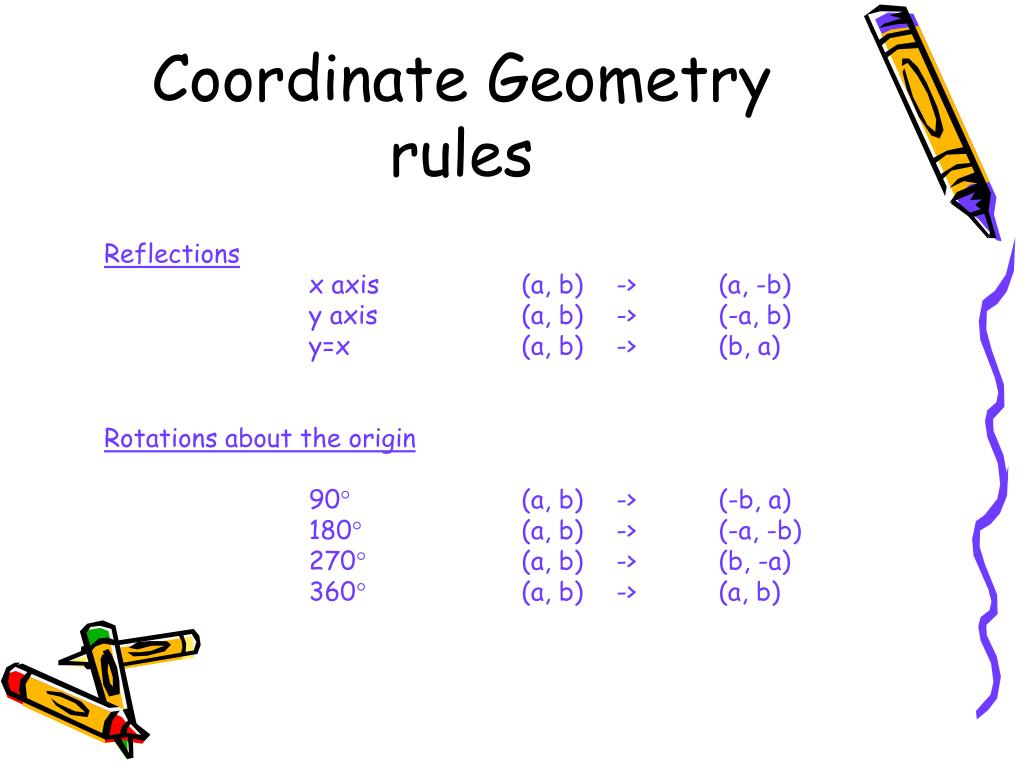
This translation can algebraically be translated as 8 units left and 3 units down.
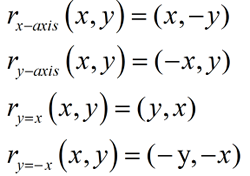
Translation of a 2-d shape causes sliding of that shape. Transformations help us visualize and learn the equations in algebra. We can use the formula of transformations in graphical functions to obtain the graph just by transforming the basic or the parent function, and thereby move the graph around, rather than tabulating the coordinate values. Transformations are commonly found in algebraic functions. Transformations can be represented algebraically and graphically. Here are the rules for transformations of function that could be applied to the graphs of functions. On a coordinate grid, we use the x-axis and y-axis to measure the movement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
